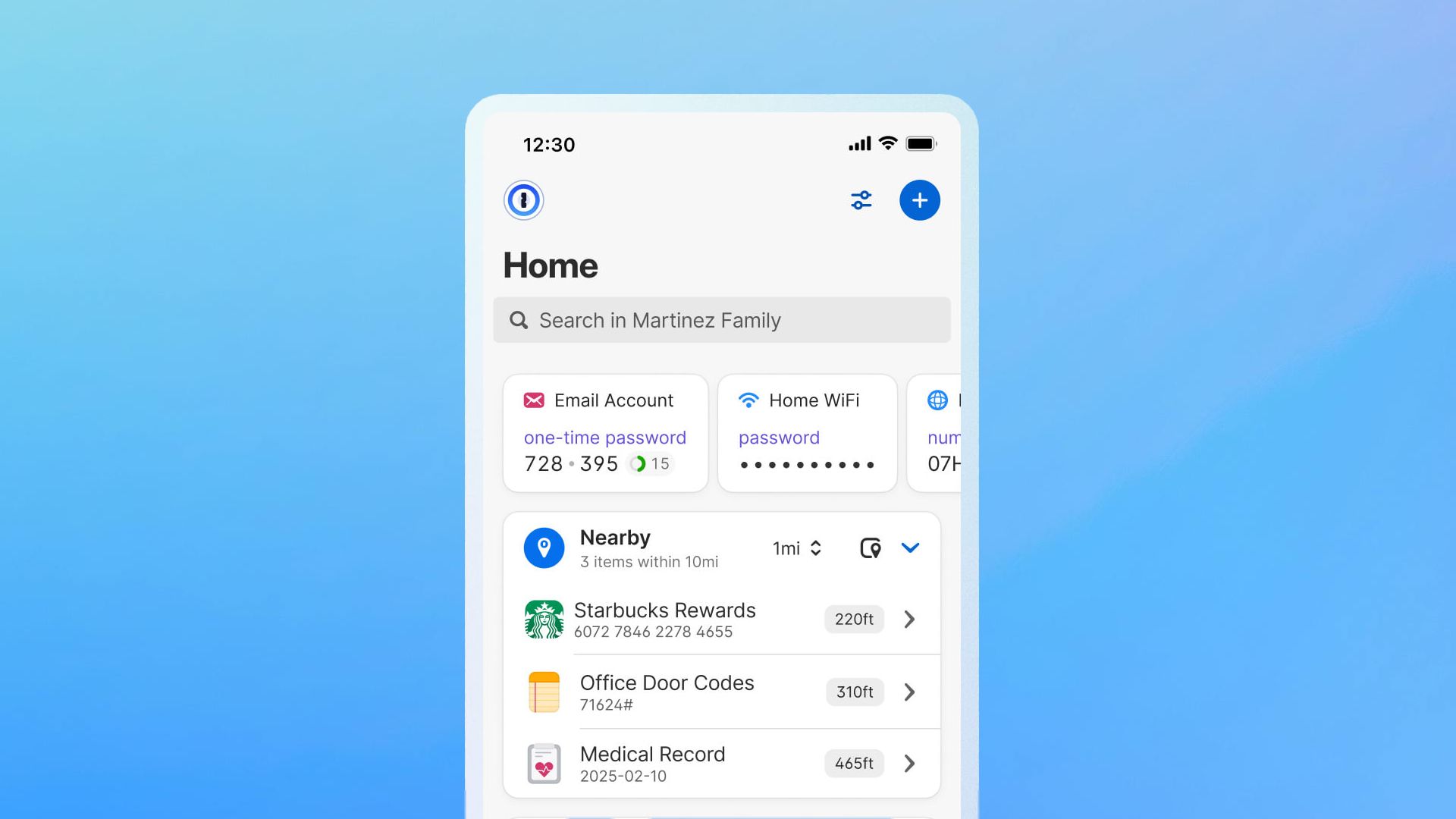
Using a password manager on your Android phone is crucial for creating and maintaining strong, unique passwords for every app and website you use. However, if you’re not careful, it can also become a security risk.

Why Password Managers Are a Double-Edged Sword
Password managers are often hailed as one of the most secure and convenient ways to manage your growing collection of logins. They generate complex passwords, store them securely, and autofill them when needed. But despite these benefits, password managers also come with their own set of risks, making them a double-edged sword.
On the positive side, password managers help you avoid reusing passwords across apps and websites, which is a significant security flaw. They also help you create strong and unique credentials.
With a password manager, you only need to remember one password—the master password—which acts as a key to your vault of passwords. These two features alone play an essential role in reducing your exposure to common attacks like credential stuffing.

Deep dive
What Is a Credential Stuffing Attack?
Here’s everything you need to know about this dangerous cyberattack and what you can do to protect yourself.
While we recommend using password managers, you should be aware of the associated risks. A password manager stores all your passwords in one place, thus creating a single point of failure.
If someone has access to your master password, they essentially have access to everything stored in the vault. That puts your digital identity at risk. Hackers can also directly target your password manager, like in the case of LastPass’s 2022 breach, where attackers compromised its security systems to gain access to personal vaults stored in the cloud.
In short, password managers are great tools, but only if used properly. Relying on them without understanding the risks can leave you just as vulnerable as having no security strategy at all.
How to Use Password Managers the Safe Way
While password managers can significantly enhance your online security, they aren’t foolproof. To truly benefit from them without exposing yourself to unnecessary risks, following best practices and understanding how to use these tools responsibly is essential.
The following tips outline key ways to ensure your password manager works for you, not against you.
Use a Reputable App
Several password managers are available on the market. However, before you click download, remember that not all password managers are created equal. Besides having all the must-have features for any password manager, choosing a well-known, reputable app is your first line of defense.
The best approach is to choose a password manager with a strong security track record, transparent security practices, regular third-party audits, and, as a bonus, one that is open-source.
Choose a trusted password manager from a reputable company that prioritizes both security and user privacy. Avoid obscure or poorly reviewed apps that lack proper encryption or have hidden vulnerabilities.
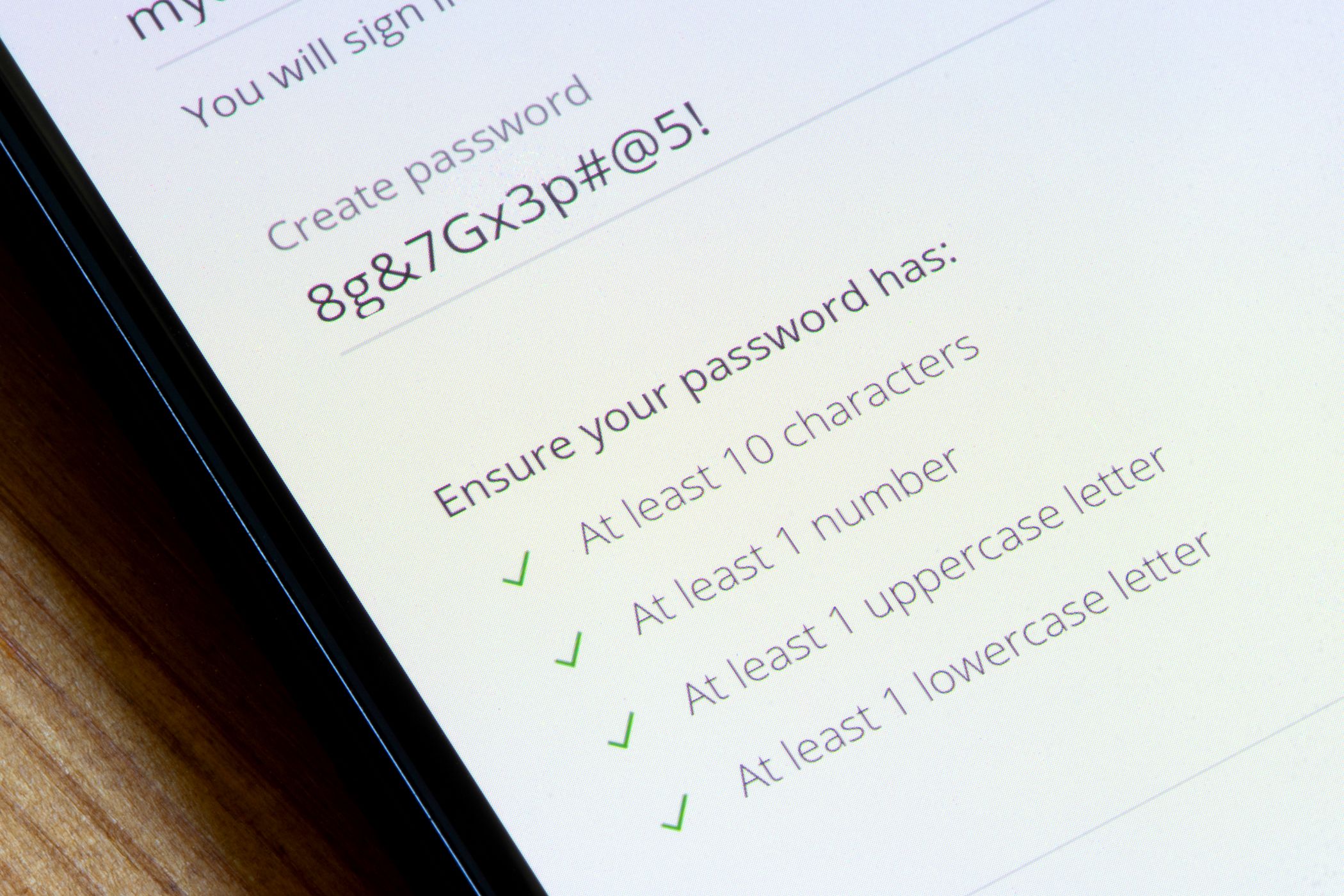
Set a Strong Master Password
Your master password is the key to your entire vault. If it’s weak, everything inside is at risk. Choose a password that is long, unique, and difficult to guess. For the master password, avoid using common words, birthdays, or personal information, such as your birthplace or pet’s name.
Instead, consider a passphrase made up of unrelated words. Ensure the passphrase includes uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters, and is at least eight characters long. This will help you avoid common mistakes people make while setting up a password manager.
You can use a password generator to create your passphrase, but avoid writing it down; memorizing it is the safest option. In addition, since this is the one password you need to remember, never reuse it for any other account. It should only be used to unlock your password manager.
Enable Auto-Lock
Auto-lock ensures your password manager locks itself after a period of inactivity or when your device is idle. This helps protect your vault if you walk away from your computer or lose your phone.
Even a short period of unattended access can be enough for someone to access your data, so setting a short auto-lock interval is a smart move. Some password managers let you customize how quickly the vault locks. For this, set it to minutes, not hours, to stay on the safe side.
Turn On Two-Factor (2FA) Authentication
Setting a strong master password isn’t enough. You also need to enable 2FA, a feature that most password managers provide. 2FA adds an extra layer of security to your password manager by requiring a second form of verification—like a code from an authenticator app or a hardware security key—alongside your master password before logging in.
This adds a layer of protection, ensuring that even if someone steals your credentials, they can’t access your vault without the second factor. Enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and is a must-have feature for keeping sensitive data safe.
Keep Your App and Android OS Updated
Regular updates patch security flaws and improve performance; keeping your password manager app and Android OS up to date is crucial. Software updates keep you safe, so never ignore them.
Developers constantly fix vulnerabilities that hackers might exploit, and staying current ensures you benefit from the latest protections. Enable automatic app updates and promptly install system updates to remain protected.
Password managers are powerful tools for protecting your digital life, but only if used wisely. Start by choosing a reputable app, setting a strong master password, enabling key security features (such as two-factor authentication and auto-lock), and keeping everything up to date. This ensures your security tool remains a safeguard, not a vulnerability.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/twoku-twtich-roku-app-2053432b763a40d788ef726974d9ed2a.png?w=1174&resize=1174,862&ssl=1)




Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *