Wi-Fi drops, especially in the middle of something important, are incredibly frustrating. My Wi-Fi was dropping almost hourly—here’s what I did to finally fix it.
7
Scheduled Restarts
Simply rebooting your router can fix tons of connection issues. Rebooting resets your router’s memory, clears out any temporary glitches, and reloads its firmware and settings. It also releases any unresponsive connections and expired IP addresses that your router’s DHCP server might be tracking.
You don’t have to set a reminder to do this manually, either. Most routers have a scheduled restart setting that automatically restarts the router at a time you specify. I recommend setting your router to reboot late at night when you won’t be using the internet. This way, any temporary downtime for your smart home devices won’t affect you.
6
Adjusting Wi-FI Channel and Frequency
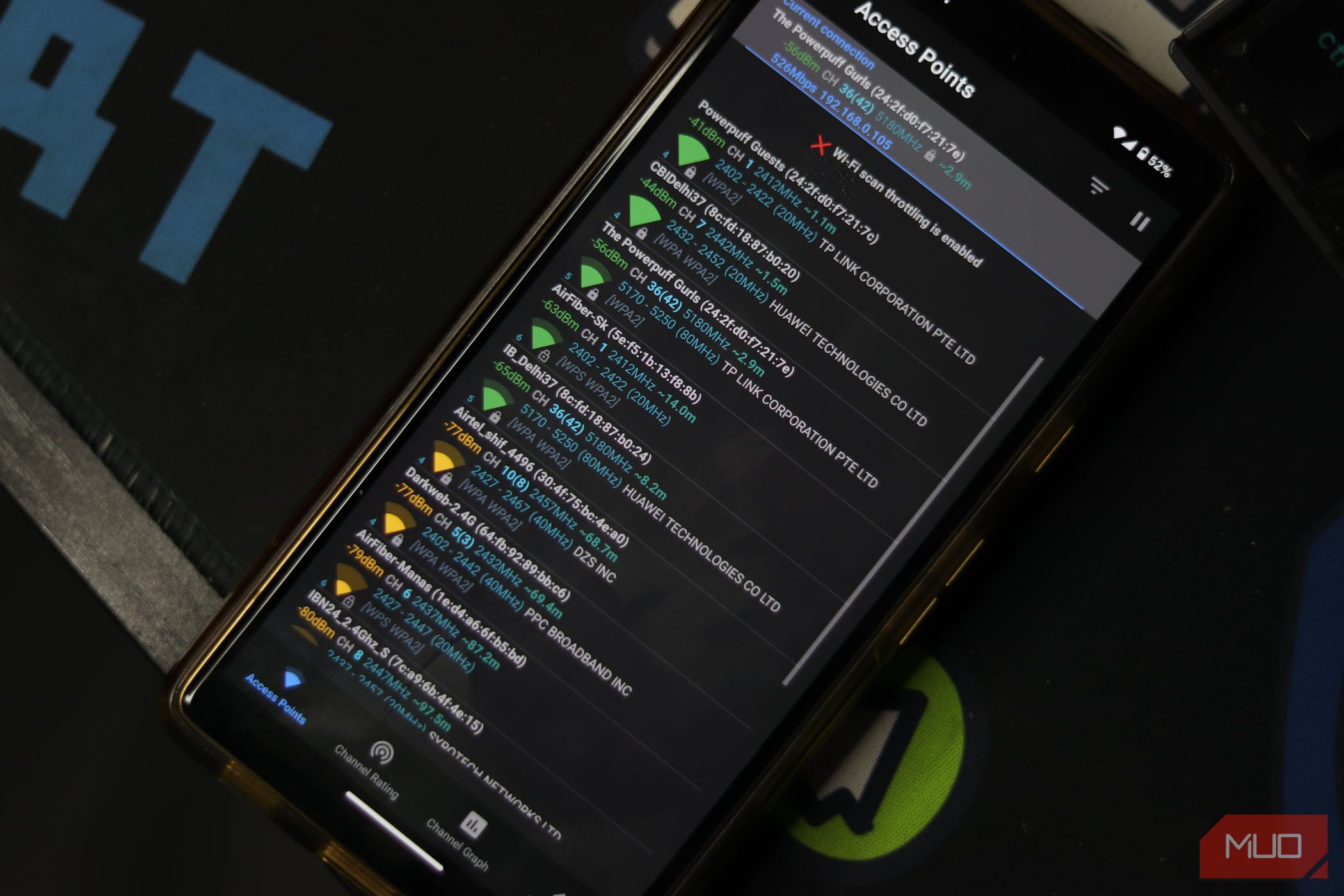
Your Wi-Fi network can get pretty crowded with phones, laptops, consoles, TVs, and other smart home devices using it to access the internet. In such cases, your Wi-Fi channel can get crowded, and if it becomes too much for the router to handle, you’ll start experiencing Wi-Fi drops.
This is called network congestion and can cause laggy internet with high jitter, packet loss, and latency. I recommend analyzing your Wi-Fi network first to determine if you’re connected to a congested channel, and then update your Wi-Fi and device settings accordingly.

Related
Network Congestion Is Slowing Down Your Wi-Fi, but There Are 2 Easy Fixes
These two small changes can make a surprising amount of difference to your Wi-Fi speeds.
As a general rule of thumb, you want to connect priority devices like your phone, PC, console, TV, or anything else that requires stable and high-speed internet to the 5GHz channel. Everything else, including your smart home devices, will do fine with the 2.4GHz channel.
If you don’t have a 5 or 6GHz channel on your router, it’s high time for an upgrade. However, you can set up QoS on your router to prioritize traffic and mitigate the issue to some extent.
5
Get the Router Placement Right
Your Wi-Fi connection’s stability largely depends on the signal strength you’re getting from the router. If your router is tucked away in a cupboard or corner of your house, you need to place it correctly. It’s the easiest way to fix your Wi-Fi without buying new gear.
Ideally, you want to place your router as centrally and as high as possible to ensure you cover the entire apartment. For bigger houses, one router might not be enough to provide Wi-Fi to each room or floor.
In such cases, you can use a Wi-Fi repeater or mesh network to extend your Wi-Fi’s range. We’ve tried both, and mesh Wi-Fi came out on top. However, using a repeater is the more budget-friendly option, as you won’t have to buy multiple Wi-Fi devices.
You can also fix Wi-Fi dead spots with an old router if you have a spare lying around. Your surroundings significantly affect the Wi-Fi signal. Materials like concrete, metal, and glass can block or reflect off signals in unwanted directions, causing random Wi-Fi dropouts or reducing your Wi-Fi’s working range. Also, make sure you’re sitting away from anything that can interfere with your router’s Wi-Fi range. Sitting right next to a working microwave won’t do wonders for your Wi-Fi signals!
4
Be Wary of Your Device’s Reception Range
Just because you get good Wi-Fi strength in every corner of your house doesn’t mean all your devices will, either. Older devices have weaker antennas that need to reduce the Wi-Fi range. For example, if your phone’s Wi-Fi signal strength is 50% in a specific spot, a weaker Wi-Fi card in a laptop or older phone might not register the signal at all.
Apart from swapping out the Wi-Fi card, if possible, there’s not much you can do here. Simply moving closer to the router is the best option here. If you like working at a desk and your system isn’t in range, running an Ethernet cable might be the best option.

Related
Why I Always Use an Ethernet Connection Wherever I Can
Wi-Fi is super useful, but Ethernet’s positives make it even better.
Another way to tackle this issue is to move the router closer—a mammoth task, considering it will affect Wi-Fi signals to every other device on the network. Using a repeater or mesh network is a much better option in this case.
3
Check Your Device Network Settings
Incorrect network settings on your device can cause Wi-Fi drops, even if your router is perfectly fine. I’d recommend resetting your network settings and clearing your cache as a first step. It’s an easy-to-follow process on most devices and can fix all kinds of problems with your Wi-Fi and even your cellular network. For example, you can clear your DNS cache on most browsers or flush the DNS cache on Windows 11. However, the same tips apply to every operating system; you may need to do an internet search to find the right steps.
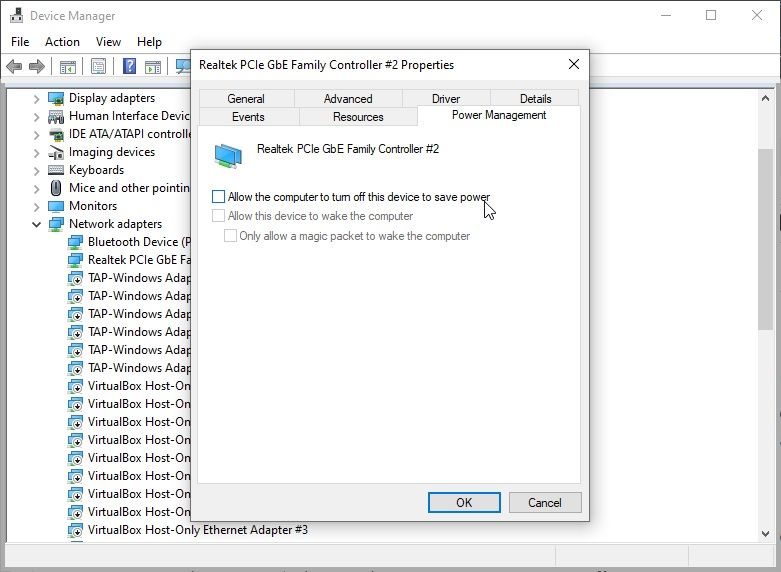
If you’re using a laptop, check your power settings to ensure your Wi-Fi card receives the necessary power for broadcasting and receiving. Windows has a knack for putting Wi-Fi cards in low-power mode, a problem you can fix in the Device Manager.
- Input device manager in the Start menu search bar and select the Best Match.
- Scroll down to Network Adapters. Right-click your Wi-Fi adapter name and select Properties.
- Now, open the Power Management tab and make sure Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power is unchecked.
Now, it’s also worth checking your Windows power settings, too. Windows power saving plans have been known to cause the same problem.
- Input power options in the Start menu search bar and select the Best Match.
- Select Change plan settings > Change advanced power settings.
- Locate Wireless Adapter Settings > Power Saving Mode, and toggle this to Maximum Performance.
While you’re at it, it’s also worth checking and optimizing your router’s settings. Most of the time, the default settings on your router will be fine, but you can extract more speed, stability, and range from it if you adjust the settings correctly (it can also make your Wi-Fi more secure!).
2
Pay for More Bandwidth
Another reason your Wi-Fi may be constantly dropping is a lack of bandwidth. If you’ve got way too many devices hooked up to the Wi-Fi and too little bandwidth, your internet connection will grind to a halt. Run a Wi-Fi speed check and consider if you need an upgrade. A 300 to 500 Mbps connection will usually suffice for a family.
One symptom to look out for is consistently slow internet speeds. Even if your Wi-Fi is working fine, if your internet speeds are slowing to a crawl, you either need to kick some devices off the network or get more bandwidth.
1
Your Router Might Be Due for an Upgrade
If you’ve gone through this list and your Wi-Fi is still dropping, you likely need to upgrade your router. Connection drops and reduced speeds are among the first signs that you need to upgrade your router.
Older routers only support the 2.4GHz band, which results in low speeds and makes them susceptible to interference from other electronic devices. Upgrading to a dual or tri-band Wi-Fi router with multiple 5 or 6GHz bands will help with both network stability and speed. Additionally, newer routers also have better software features that’ll help keep your network secure and stable.










Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *