Still using “123456” or your birth year as a password? It’s time to stop. Using weak and commonly used passwords is one of the main reasons why you can be hacked. Fortunately, you can easily level up your password game with these steps.

1
Acknowledge the Problem
The first step to better password security is admitting that your current habits might not be secure enough. But how will you know? Several telltale signs indicate you have a password security issue, including:
- Using the same password for multiple accounts
- Saving your passwords in a notebook
- Including personal information in your passwords
- Choosing passwords that are easy to remember
If any of those apply to you, your current password habits are putting you at risk. Now that you’ve identified the issue, it’s time to make your passwords much stronger and safer.
2
Pick a Password Manager
After acknowledging the issue, the next step is to let technology do the heavy lifting. We’re not in the early ages of the internet when most folks had just a handful of accounts. Currently, you probably have tens of accounts online, and a password manager is vital for keeping track of all those unique passwords.
In a nutshell, a password manager is an application that stores all your login credentials in a secure, encrypted vault. It provides a more convenient and secure way to store and generate passwords.
This will be the central location where you’ll store passwords for all accounts. Additionally, modern password managers can generate strong and secure passwords and include features like password sharing for added convenience.

Related
What Is the Safest Password Manager to Use?
Looking to keep your login credentials secure? You need to know the safest password managers for Windows, Mac, iOS, Android, and more.
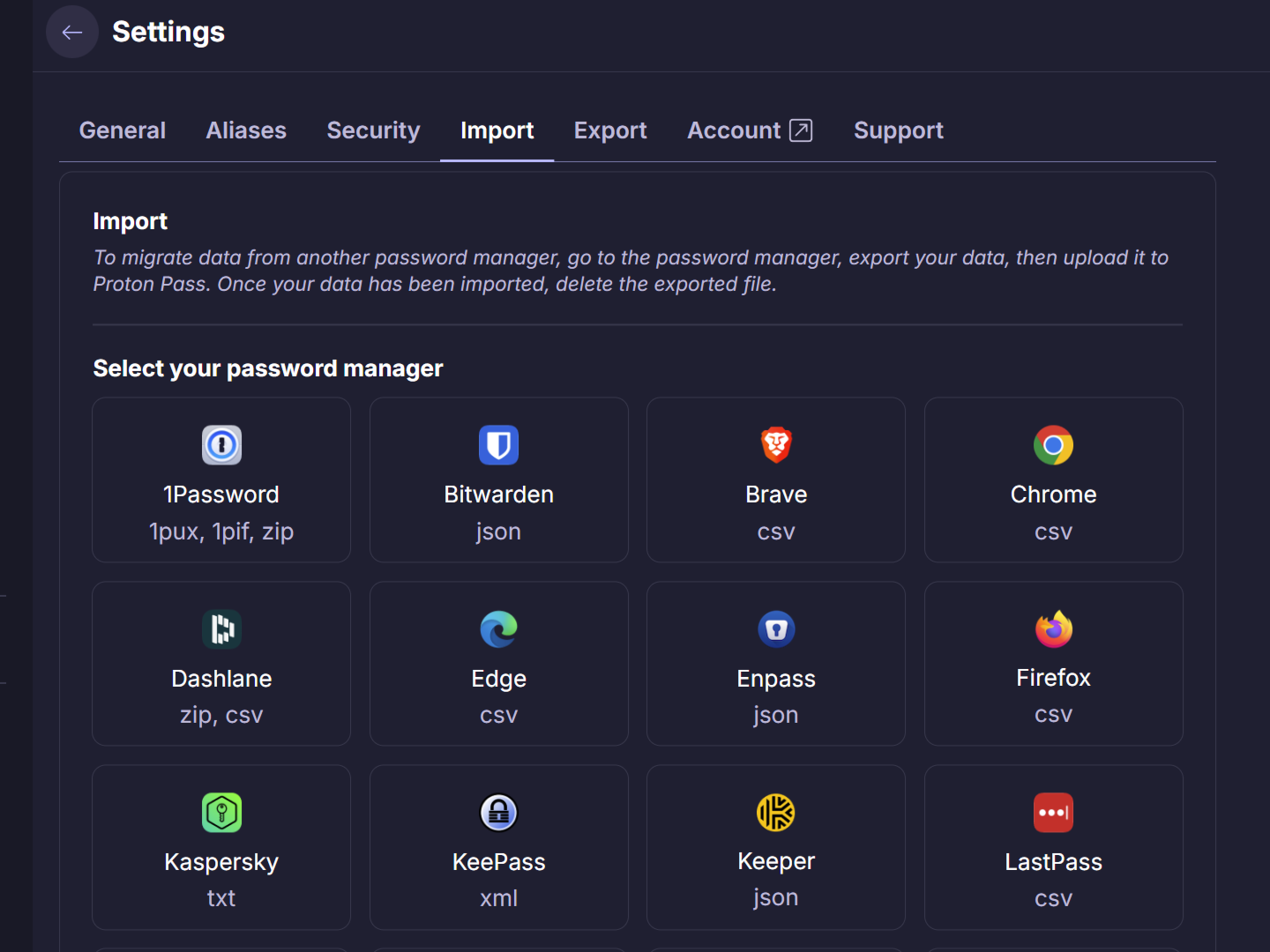
That said, there are numerous password managers available. The most prominent options include Bitwarden, Dashlane, 1Password, NordPass, and ProtonPass—all of which offer the must-have features you need in a password manager.
3
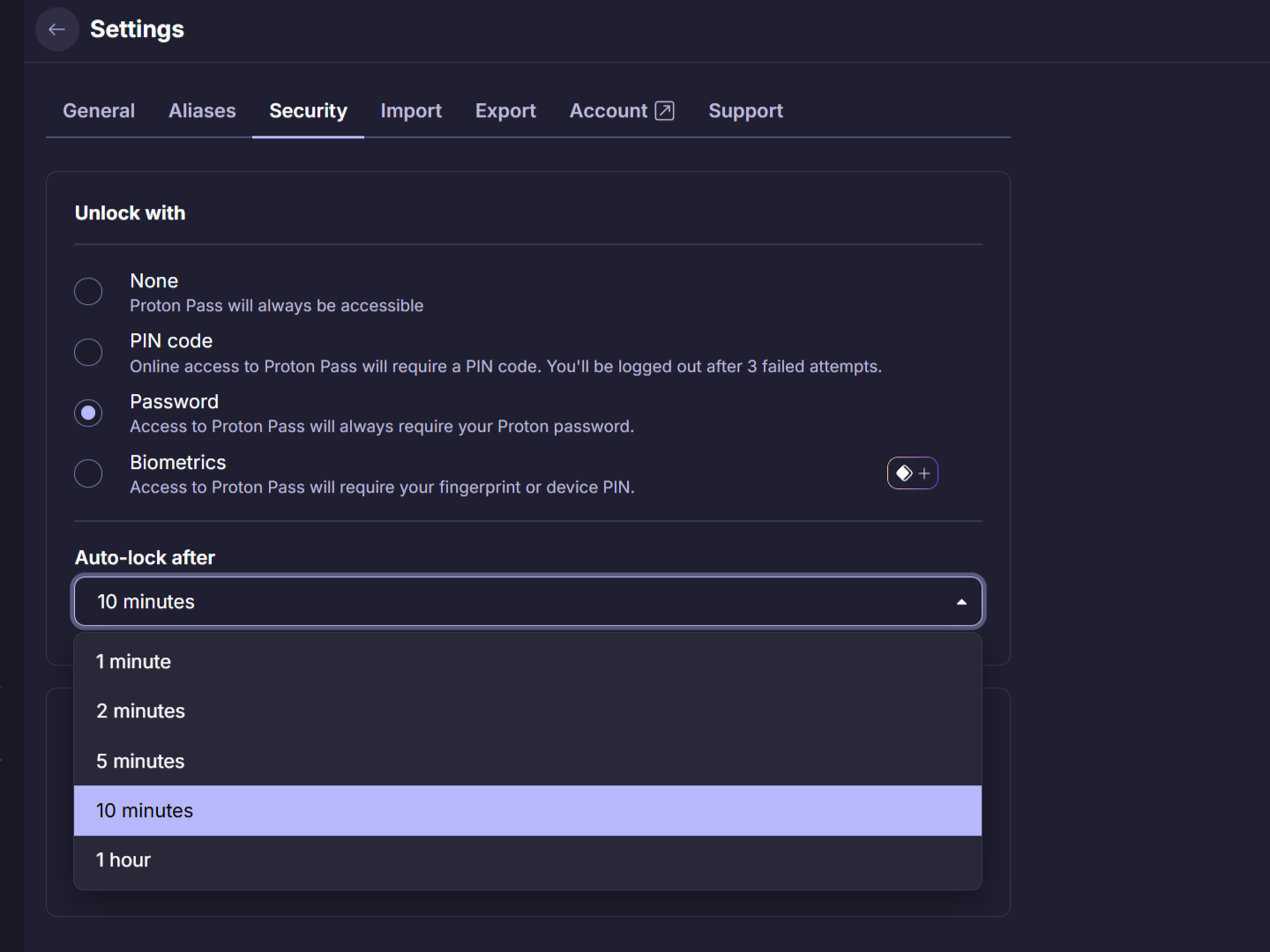
Set Up Your Password Manager
Once you settle on a password manager, it’s time to set it up. Start by creating a strong master password, which is the password you’ll use to unlock your password manager. The master password is the one you need to remember, so make it long, unique, and hard to guess—so no birthdays or pet names.
The best approach is to use a passphrase, which will help you avoid the common mistakes made when setting up a password manager. A passphrase is a sequence of words typically longer than a password used for authentication. Come up with a unique and memorable sentence, then twist some letters with special characters here and there for a strong master password. For example, 1Lik3Sunshine$Over-Mountains42 is a passphrase that is long, memorable, and includes numbers, symbols, lowercase, and uppercase letters.
Be sure to set a recovery email, which will help you regain access if you forget your master password. Finally, install your password manager’s applications on your device. Install the desktop and mobile apps, and for your preferred desktop browser, install the browser extension (if available).
4
Begin Migrating Your Existing Passwords
The best password managers provide ways to help you import passwords from your browser or other password managers. However, when starting from scratch, you can only add your existing passwords manually.
If you have many accounts, don’t feel the need to add all your accounts at once—you can migrate a handful of accounts daily. The best approach is to start with your most important accounts, like your email, bank, social media, shopping sites, and work-related accounts.
For the remaining sites, you can slowly let your password manager automatically save your login when you visit any of them and log in or sign up. Over time, your password manager will store login details for all your accounts. And once you reach that point, it becomes a good time to back up your password manager.
5
Enable Additional Security Features
With your passwords stored in one single place—your password manager—the next step is to enhance the security of your password vault. First, enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for your password manager.
Even if your master password is compromised, 2FA adds an extra layer of protection to keep your vault secure. Some password managers also offer you an option to re-enter the master password before viewing a specific password.
6
Maintain Strong Security Habits
Using a password manager to store your passwords is a good foundational step. But it doesn’t end there. Going forward, it’s essential to have a system in place to ensure the security of your vault and passwords.
This includes reviewing your passwords quarterly, updating your critical passwords every three to four months, and regularly updating your password manager. Some password managers also offer security analysis, also known as password vault health, to identify weak or duplicated passwords. Ensure that you utilize them.
You should also avoid reusing passwords and use a password manager to generate strong, secure passwords.







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-use-a-router-as-a-wifi-extender-7c5255410be4463d978ada19db9673c0.jpg?w=1174&resize=1174,862&ssl=1)

Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *